How mortgage rates impact your mortgage payments


The rate on your mortgage – fixed or variable, directly impacts your mortgage payment. In the case of a variable-rate mortgage, when mortgage rates are increasing your payments increase and the reverse holds for decreasing mortgage rates. While fluctuations in the current prime rate in Canada will only impact payments on a fixed-rate mortgage when it is renewed at the end of its term.
Many homeowners will be either positively or negatively impacted by changing mortgage rates – which depends on the direction of the rate changes. It is important to know just how you will be impacted by looking at the increase in your mortgage payment and breaking it down by which portion is going to interest and which to principle.
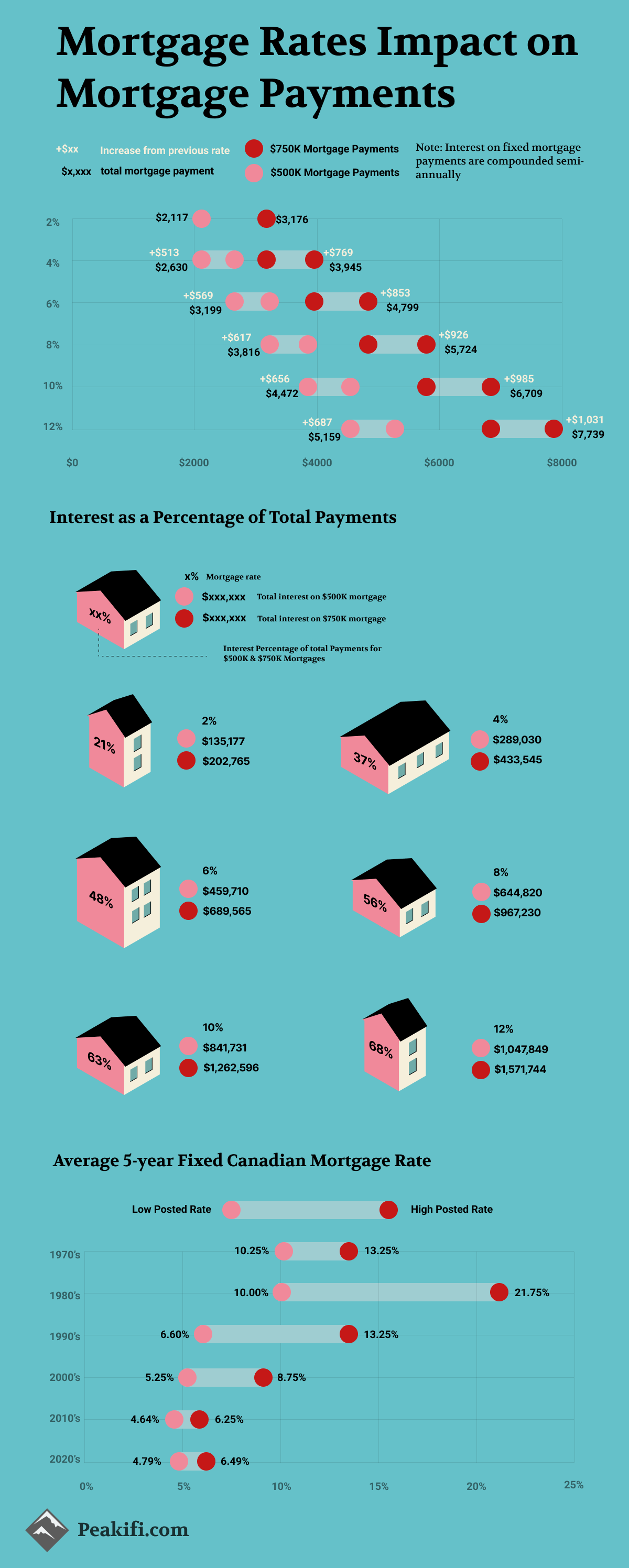
The infographic represents a visual of the relationship between payments on a $500K and $750K fixed Canadian mortgage and various fixed mortgage rates. This helps to provide you with a visual reference of what you can expect to happen to your mortgage payments – when you renew your mortgage at the market rates.
Increases in mortgage rates directly impact the amount of interest that you pay on your mortgage payment – and the total mortgage over the amortization period. This visual shows you how much each incremental interest rate increase will increase your mortgage payment and the increase in interest that you will experience.
Further, we wanted to show the relationship between the total interest paid over the lifetime of the amortization period of the mortgage compared to the overall total payments (total Interest + principal repayment). This helps to show how small increments in mortgage rates can have a large impact on the total interest paid – as well as the total interest as a percentage of total payments. The relationship between the total interest paid and the total payments is consistent independent of the mortgage size.
Lastly, we wanted to add the average 5-year Canadian mortgage rates over the past six decades to help show the different possible combinations of rates and what mortgage payments would have been at these levels.
What percentage of your mortgage will be interest payments?
For both the $500K and the $750K fixed mortgages, the interest percentage of total payments is the same for each mortgage rate – with the total amount of interest being different given the varying sizes of the mortgages. When mortgage rates are 2% interest payments make up 21% of the total payments for a mortgage for a total of $135,177 on a $500K mortgage and $202,765 for a $750K mortgage. This percentage of interest payments of total payments increases substantially as rates increase. This impact can be shown as we move up to a mortgage rate of 12% - which is six times the 2% mortgage rate. At a 12% mortgage rate, the total interest on a $500K mortgage increases to $1,047,849 which is more than six times the interest paid on the 2% mortgage rate. This impact can also be seen on the $750K mortgage as the total interest paid increases to $1,571,744 – both of these mortgages make interest payments that make up 68% of the total payments made when mortgage rates are 12%.
How are variable mortgage rates determined in Canada?
Variable mortgage rates are directly impacted by the Bank of Canada (BoC) policy rate – which acts as the benchmark for lenders to determine variable mortgage rates in Canada. When the BoC makes increases to their policy rate, it will in turn directly impact the prime rate that is used in determining mortgage payments on variable-rate mortgages. Variable mortgage rates are usually less than fixed mortgage rates since you are exposed to market rate fluctuations.
How are fixed mortgage rates determined in Canada?
Fixed mortgage rates are set by the lender and remain for the full period of your mortgage term – with the typical mortgage term in Canada at five years or less. The shorter mortgage term in Canada exposes borrowers to the current market rate more often. It is only upon the renewal of your fixed rate term that you will see your mortgage payments change. The fixed rate is influenced by the Bank of Canada (BoC) bond yields over a similar term as the mortgage with a markup to allow lenders to make a profit.
How mortgage rates impact the price of the house you can afford
When mortgage rates increase – so does the amount of interest that needs to be paid on the money that is borrowed for a mortgage on a property. If you already have a mortgage, you will see this increase directly in your mortgage payment if you have a variable-rate mortgage or when you renew your fixed-rate mortgage. For those who are looking to purchase their first home, mortgage rates will directly influence how much the bank is willing to loan. When rates are low, you will be able to borrow more money which will allow you to purchase a higher maximum home price. When these rates increase, your maximum home price will be lowered.
How often does the prime rate change in Canada?
The prime rate in Canada has the potential to change eight times a year. The prime rate is directly related to the policy rate in Canada which is set by the Bank of Canada (BoC). The policy rate is scheduled to change on the following dates for 2024.
- January 24, 2024
- March 6, 2024
- April 10, 2024
- June 5, 2024
- July 24, 2024
- September 4, 2024
- October 23, 2024
- December 11, 2024